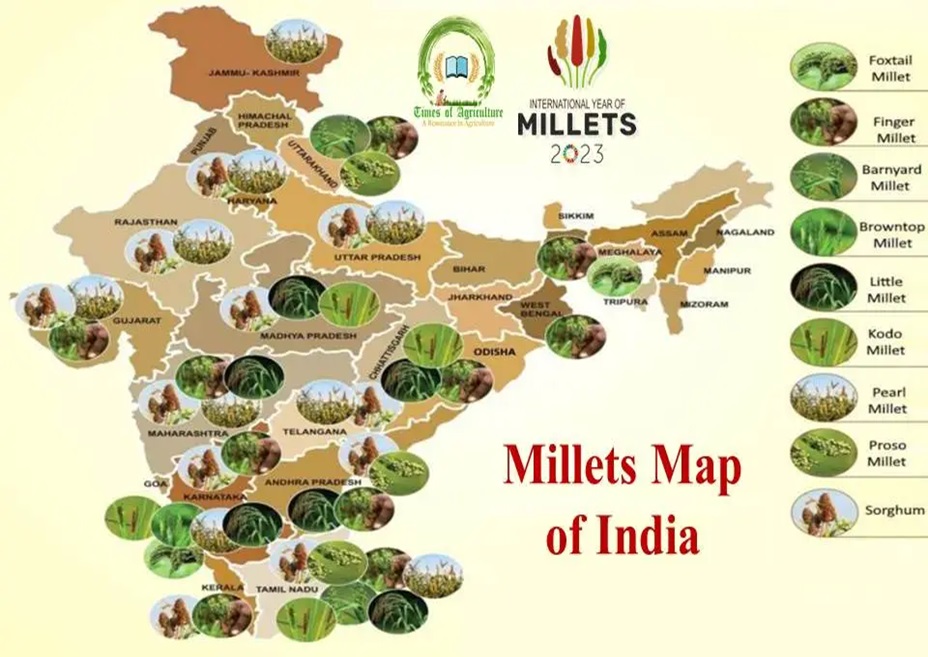
Indian Millets

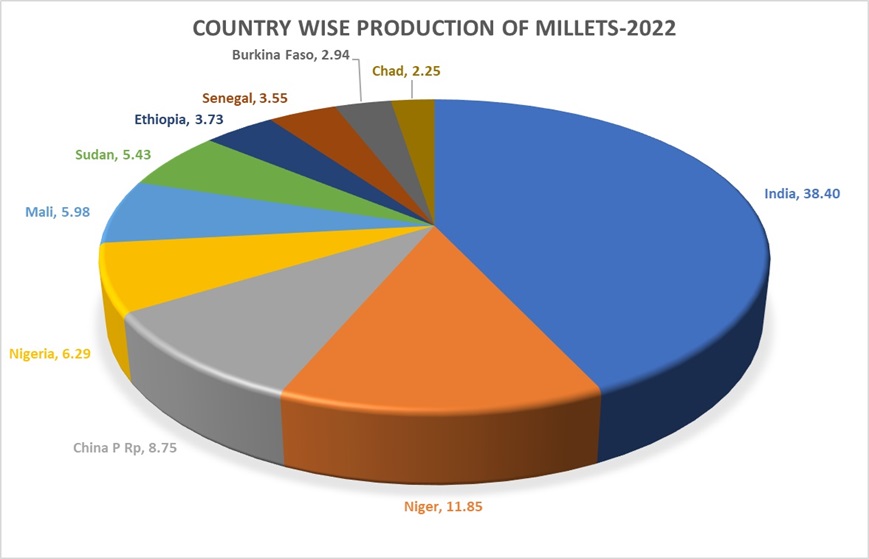
Millets as a Subhead consists of Sorghum (jowar), Pearl millet (bajra), Finger Millet (ragi), Banyard Millet, Proso Millet, Kodo Millet, Buckwheat, Amaranthus and Foxtail Millet. Being excellent source of essential nutrients to the millions of Indians, they are also called as ‘nutritious cereals’. The Indian Millets are nutritionally superior to wheat and rice as they are rich in protein, vitamins and minerals. They are also gluten-free and have a low glycemic index, making them ideal for people with celiac disease or diabetes. India is the world's Largest producer of Millets with the share of 38.40% of worlds production.(Source:Food & Agricultural Organisation (FAO) (Updated as on 01-12-2023)). |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
The products under the category of Maize are as below: |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Benefits of Millets:
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Millet Producing States: |
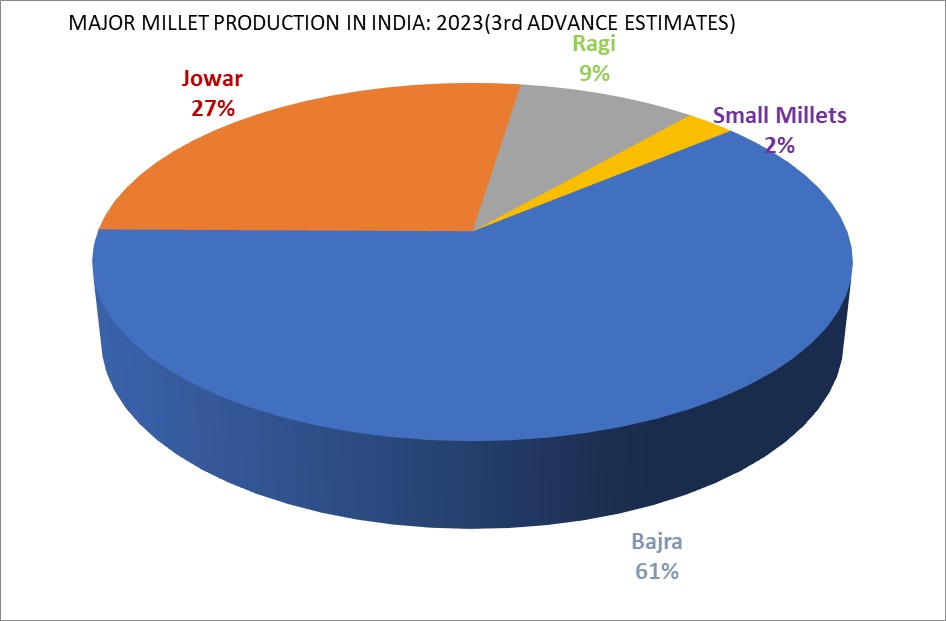
The major millets producing states in India are Rajasthan, Karnataka, Maharashtra, Uttar Pradesh, Haryana, Gujarat, Madhya Pradesh, Tamil Nadu, Andhra Pradesh and Uttarakhand. Currently, together these ten states account for around 99 per cent in Millet’s production in India during the period 2023-24 (3ⁿᵈ Advance Estimates). |